Genetic Science
细胞遗传学是研究科学。它furthers our understanding of how DNA and the genetic make-up of species and can lead to cures for diseases and shape our future.

为什么人们在淋浴的时候唱歌吗?

10 Bizarre Treatments Doctors Used to Think Were Legit

Ancient Egyptian Pregnancy Test Survived Millennia Because It Worked

Can You Crack This Nuts Quiz?

The Science Behind Your Cat's Catnip Craze

Clever App Uses Smartphone Camera to Identify Plant Species

Your Phone Is a Germ Factory, So Stop Taking It to the Toilet

Why Even Identical Twins Have Different Fingerprints
Which Emerged First: Viruses or Living Cells?

Howstuffworks Interviews: Extinction Level Events with Annalee Newitz

What's the worst extinction in Earth's history?

Why did Neanderthals become extinct?

Why can't we remember being babies?

The Big, Bad Brain Quiz

No More Sweet Tooth? Science Turns Off Sugar Cravings in Mice
Learn More / Page 2
Hereditary illnesses are passed down from parents to their children like gene traits, and children might inherit a disease even though their parents never suffered from its symptoms. Learn about hereditary illnesses.
Genetically modified organisms have been around for centuries, but the controversy is really about foods that have been modified in the lab. Should we be worried about eating them?
It's a chicken-or-egg situation: What came first? Perplexed people need wonder no longer, as we've sussed out the answer to this ancient riddle.
Advertisement
Cloning is the process of making a genetically identical organism through nonsexual means. In this article, we will examine how cloning works and look at possible uses of this technology.
What is the difference between a hardwood and a softwood? How hard does a tree have to be to be considered hardwood?
With movie titles like "Attack of the Clones" and "The Clone Wars," it's no wonder human cloning makes us anxious. As scientists make startling discoveries cloning animals, are humans next?
By Kevin Bonsor &Cristen Conger
That bowling ball of white meat in your oven is a far cry from its wild ancestors. How did a single breed of top-heavy, dim-witted birds come to dominate the turkey market?
Advertisement
The field of epigenetics investigates how environment, nutrition and social conditions affect gene expression. Does that mean DNA isn't destiny?
You know how scientists labored to map the human genome? Well, they're back at it, only this time, they're studying what causes those thousands of genes to switch on and off.
Imagine strolling down the halls of a vast library, the shelves packed with prime genetic material from society's best scholars and athletes. Is it ever going to happen?
The Missyplicity Project sprang from one billionaire dog owner's desire to have his canine best friend back again. Did the project work, and how much are cloned animals like the original?
Advertisement
You probably feel like you have very little in common with that banana lying on your kitchen counter. But science says you do! So, how is this possible? And is that stat accurate? We talk to the scientist who did the research.
With cemetery space at a premium and the increasingly evident environmental drawbacks to traditional burial, what better way to memorialize your beloved pet, or a beloved person, than to turn their remains into a tree?
It's one of those words that might remind you of certain gender-bending musicians from the '80s, but what does it mean today?
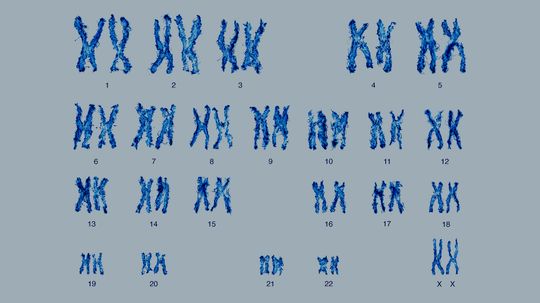
Nearly every living cell is made of DNA, and every chromosome contains exactly one molecule of DNA. But not all cells are made of the same number of chromosomes.
Advertisement
Humans are a diverse lot. We can look distinctively different. But is that because of race or ethnicity?
Cell division can be confusing, but it's not as difficult if you pretend chromosomes are sentences.
DNA websites can give you info about your ancestry and possible health issues. They can also give you trait reports about taste preferences and personal habits. But how much of that is really DNA-driven?
Epigenetics – instructions on how your genes are read and whether they are expressed or not – proves that your body is not permanently set on a specific course from the moment you're born.
Advertisement
From solving a mystery to clearing up issues of paternity, exhuming a corpse can provide answers.
Scientists are banking frozen DNA in the hope of saving endangered animals in the future.
Chimps share almost 99 percent of our genetic makeup. What makes up that tiny, 1 percent difference? What are the things that differentiate us from other great apes?
One day you can digest dairy, and the next, milk makes you sick. The culprit behind this crime against milk? Gene regulation. But how do certain traits just switch off?
Advertisement
At least two commercial DNA testing services offer users information on heritage coming from coupling between ancient humans and other species.
Mapping the genome of the King of Fruits reveals the source of its smell, and may present opportunities to develop pharmaceuticals.